DAX Function Guide
VAR
Sam McKay
CEO & Founder
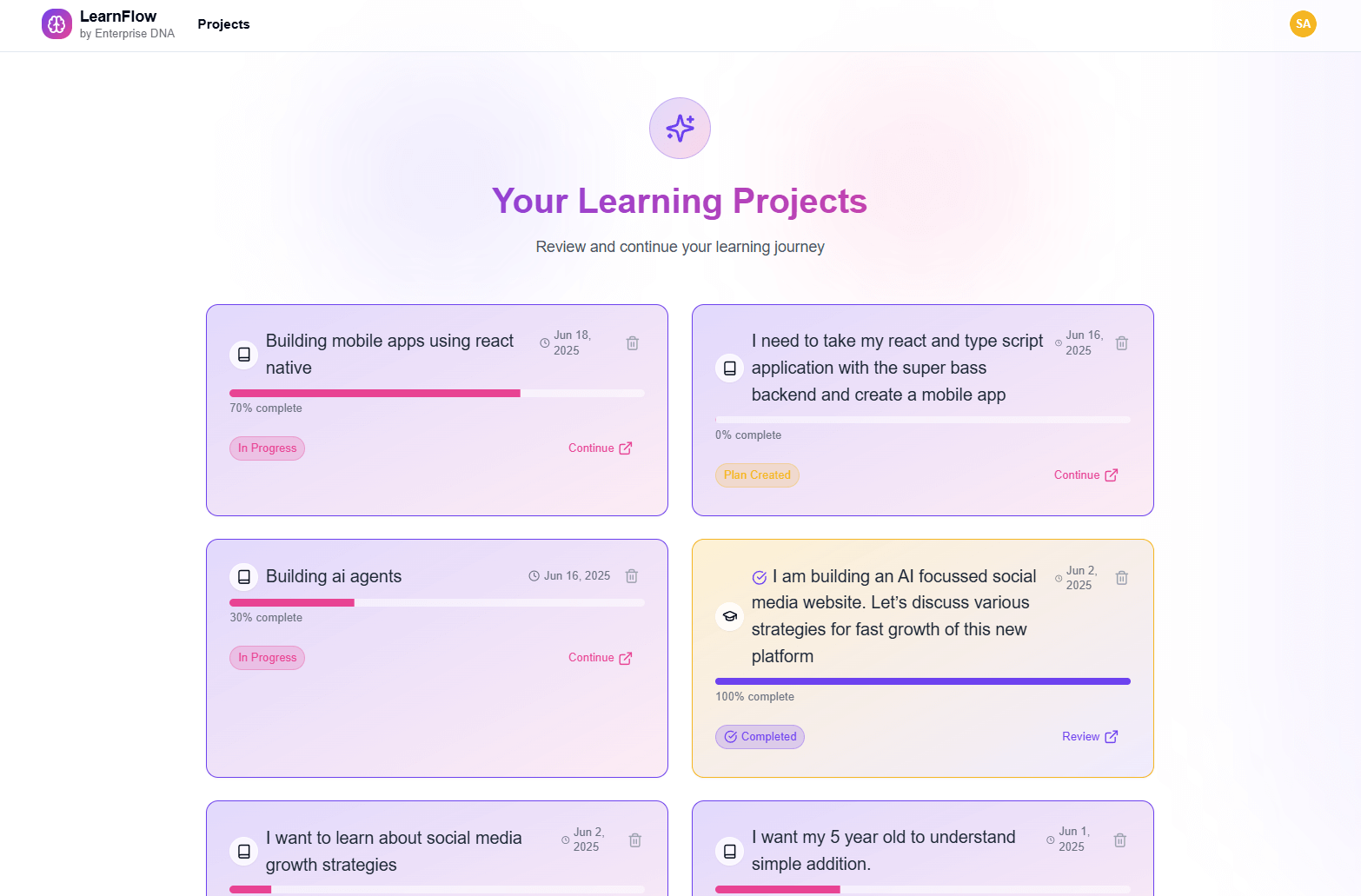
How does the VAR work?
The VAR function (DAX) stores the result of an expression as a named variable, which can then be passed as an argument to other measure expressions. Once resultant values have been calculated for a variable expression, those values do not change, even if the variable is referenced in another expression.
VAR Formula Syntax
VAR <name> = <expression>
How do you use the VAR?
The VAR function estimates the variance for a sample of data. Variance provides a general idea of the spread of data. VAR will evaluate logical values, and text representations of numbers hardcoded directly as arguments.
Related Blog Posts
Loading
Considerations when using the VAR?
- VAR assumes arguments a sample of data, not entire population. If data represents the entire population, use VAR or VAR.P
- VAR only evaluates numbers in references, ignoring empty cells, text, and logical values like TRUE or FALSE.
- Arguments can either be numbers or names, arrays, or references that contain numbers.
- Arguments can be hard-coded values instead of references.
- To evaluate logical values and/or text in references, use the VARA function.
Related Video Tutorials
Loading
Formula examples using the VAR
=VAR(34.5, 2, 8.9, -4)
=VAR(C5:C10)
=VAR(C2, C3, C4, C5)
Related Courses
Loading